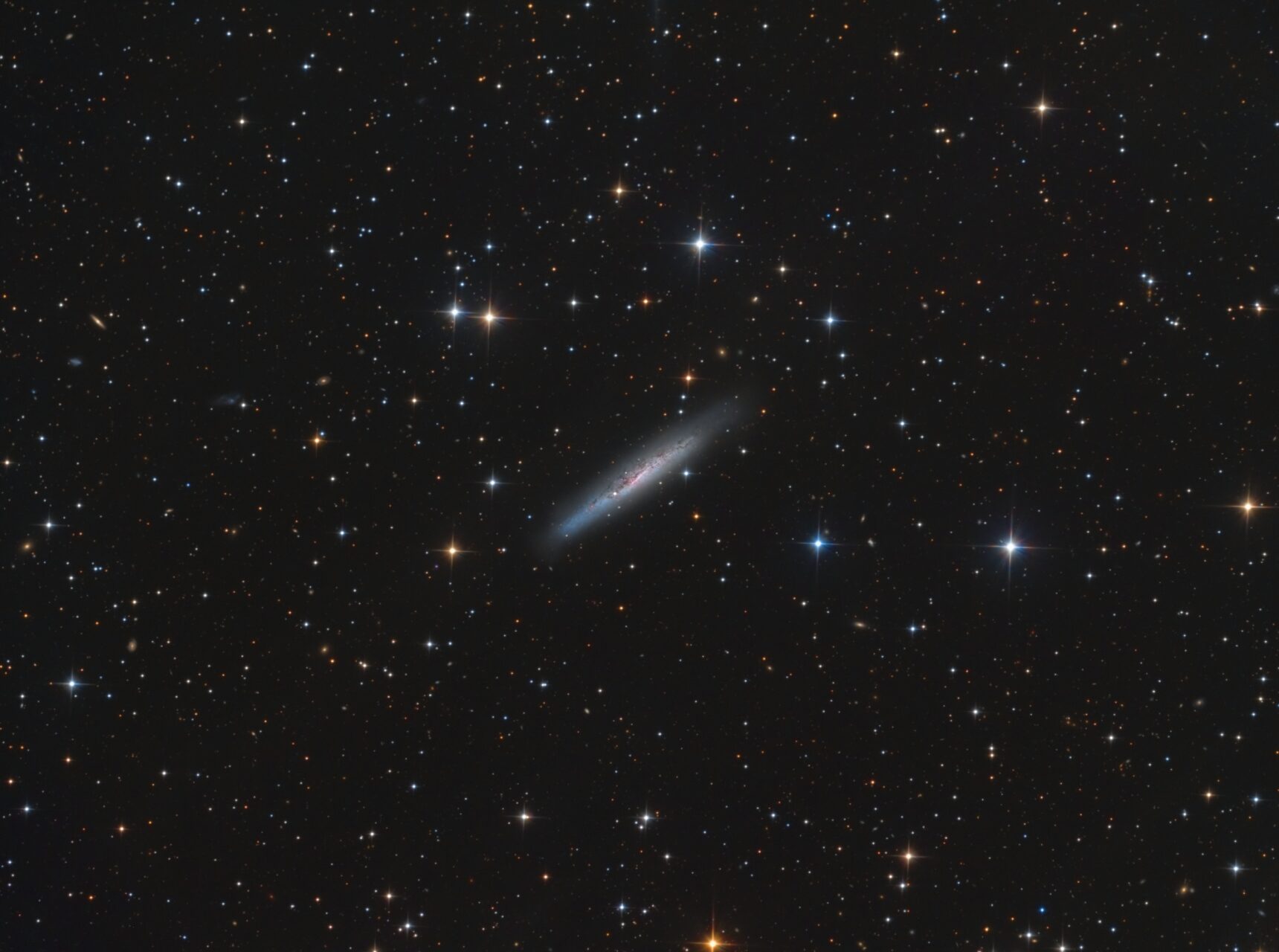
NGC 5090 and NGC 5091 are a set of galaxies approximately 160 million light-years (50 million parsecs) away in the constellation Centaurus. They are in the process of colliding and merging with some evidence of tidal disruption of NGC 5091.
NGC 5090 is an elliptical galaxy while NGC 5091 is a barred spiral galaxy. The radial velocity of the nucleus of NGC 5090 has been measured at 3,185 km/s (1,979 mi/s), while NGC 5091 has a radial velocity of 3,429 km/s (2,131 mi/s). NGC 5090 is associated with the strong, double radio source PKS 1318-43.
Two supernovae have been observed in NGC 5090:
- SN 1981C (type unknown, mag. 14.5) was discovered by José Maza on 2 March 1981.
- SN 2025cy (type Ia, mag. 18.03) was discovered by BlackGEM on 1 January 2025.
See also
- ESO 269-57
- NGC 2207 and IC 2163
- NGC 6872 and IC 4970
- List of NGC objects (5001–6000)
References
External links
- "Of Holes in the Sky and Pretty Galaxies" by the European Southern Observatory
- NASA Astronomy Picture of the Day: Seeing Through Galaxies (5 December 1997)
- NGC 5090 and NGC 5091 on WikiSky: DSS2, SDSS, GALEX, IRAS, Hydrogen α, X-Ray, Astrophoto, Sky Map, Articles and images